Biometric Technology has contributed tremendously to boosting the advancement in digital electronics. It has made it easier to authenticate a trusted user. More importantly, it has sped up the authentication process and it is 100% secure when multiple authentication methods are used together. Despite the fact that there exist some drawbacks, it is a boon to the digital world. To understand its significance, you can compare the age-old pattern-based authentication and one-touch finger scan on your smartphone.
Biometrics comprises methods for uniquely recognizing humans based on one or more intrinsic physical or behavioral traits. Certain characteristics of every human being such as fingerprint, iris, retina, voice, face, and DNA differ from each other. Biometric authentication makes use of these characteristics to identify individuals. In information technology, in particular, biometrics is used as a form of identity access management and access control. Biometric Technology is also used to identify individuals in groups.
Biometric characteristics can be divided into two main classes: Physiological and Behavioral.
- Physiological: This is related to the shape of the body. Examples include fingerprint, face recognition, DNA, hand and palm geometry, iris recognition, etc.
- Behavioral: This is related to the behavior of a person. Examples include typing rhythm, voice, and gait. Some researchers have coined the term behaviometrics for this class of biometrics. Strictly speaking, the voice is also a physiological trait because every person has a different vocal tract, but voice recognition is mainly based on the study of the way a person speaks, commonly classified as behavioral.
Suggested Read:
How does biometric authentication work?
Biometric authentication is a two-step process.
- In the first step, the biometric information from an individual is captured and stored. This is called the enrollment phase.
- In the second step, the stored data is detected and compared with the information stored at the time of enrollment. If the data matches then the user is considered to be authentic.
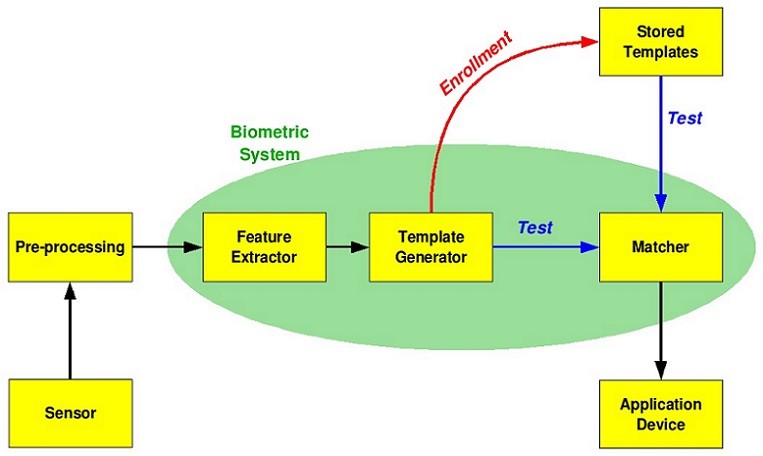
The following picture explains the biometric authentic process. (image source – wiki)
Every biometric authentication process needs a device/sensor to read input samples. This data is called a template. For a single biometric authentication method, thousands of image combinations are generated. Biometrics system makes use of database storage to store a combination of templates.
The authentication process is divided into verification and identification modes.
In the verification mode, the following three steps are involved.
- In the first step, reference models for all the users are generated and stored in the model database.
- In the second step, some samples are matched with reference models to generate the genuine and impostor scores and calculate the threshold.
- The third step is the testing step. This process may use a smart card, username or ID to indicate which template should be used for comparison.
In the identification mode, the system performs a one-to-many comparison against a biometric database in an attempt to establish the identity of an unknown individual
Commonly used Biometrics are:
- Fingerprints – A fingerprint includes patterns found on a fingertip. There are a variety of approaches for fingerprint verification, such as the traditional police-based method and using pattern-matching devices. Fingerprint scanning seems to be a good choice for in-house systems. It can be easily found on smartphones and laptops.
- Hand geometry – This involves analyzing and measuring the shape of the hand. It might be suitable where there are more users or where the user accesses the system infrequently. Accuracy can be very high if desired, and flexible performance tuning and configuration can accommodate a wide range of applications. Organizations are using hand geometry readers in various scenarios, including time and attendance recording.
- Retina – A retina-based biometric authentication involves analyzing the layer of blood vessels situated at the back of the eye. This technique involves using a low-intensity light source through an optical coupler to scan the unique patterns of the retina. Retinal scanning can be quite accurate but does require the user to look into a receptacle and focus on a given point. It is mainly used in high-security laboratories to permit only trusted users.

- Iris – An iris-based biometric authentication involves analyzing features found in the colored circular tissue that surrounds the pupil. The color of the iris determines the color of the eye. This uses a conventional camera element that helps to capture high-resolution images depicting the structure of the iris. Further, it is more reliable and results in highest pattern matching.
- Face – Facial recognition involves identifying a person based on the high-resolution images captured. Thousands of patterns of the face are captured by the facial recognition device and stored in its database. In subsequent uses, this data is used to match and authenticate a person. This kind of matching is mostly used in the police and intelligence departments. Read more on Face Identification and Recognition.

- Voice – Voice biometric authentication is on the edge of replacing other methods because of its simplicity. In this method, the user needs to speak through a microphone and the software stores the user’s voice samples. In subsequent uses, the stored records are used to authenticate a user. Voice biometrics is to replace the currently used methods, such as PINs, passwords, or account names. But the voice will be a complementary technique for finger scan as both are fast and simple enough to authenticate a user. Barclays Wealth and Investment Management is first in the world to introduce voice-based authentication to verify customers automatically as they speak. Google Assistant application introduced in Android nougat 7.0 is the first one to use voice biometrics to unlock smartphones and assist the user in google searches. This enhances the search experience.
Disadvantages involved in Biometric Technology are:
- Security of the biometric data: It is crucial that the storage and retrieval of the biometric data is highly secured. There is a chance that the thieves will stalk and assault the property owner to gain access. With the increase in cybercrimes, and ransomware attacks such systems must be kept under high surveillance and the data should be encrypted using custom algorithms.
- Biometric data cannot be re-issued: If unusual activity is detected against your account passwords, PINs can be re-issued and your account can be reprotected but in the case of biometrics, you cannot do that. If someone’s face is compromised from a database, you cannot cancel or reissue it.
- Biological characteristics may change: With age and growth certain physiological characteristics may change and the biometric authentication may not work. One has to keep updating the records over a period of time.
- The match may fail: There could be a case that the system may find a few identical records and may not be able to finalize the match.
Biometric Devices:
There are thousands of biometric devices readily available in the market. To name a few:
- Biometric Attendance Management System
- Safran Morpho Bio-metric Fingerprint Scanner
- 3M Cogent High Speed Dual Iris Scanner
- Yale Premium Biometric Fingerprint Digital Door Lock

Wrapping up:
This technology is getting better every day and spreading globally at a faster rate. Voice and fingerprint authentication is being collaborated with most electronic devices. In recent times, biometrics based on brain (electroencephalogram) and heart (electrocardiogram) signals have emerged. We hope for many such advancements in the field of biometrics.
Of course, every technology has some drawbacks, we should concentrate on overcoming these drawbacks instead of crushing the technology.