With the ever-increasing sophistication of cyber attacks, it’s becoming more and more important to have robust security measures in place to protect your computer network. One of the most effective ways to do this is through an intrusion detection system (IDS). In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what an IDS is, how it works, and why it’s essential for maintaining the security of your network.
What is an Intrusion Detection System?
An IDS is a security tool designed to monitor network traffic and detect any suspicious or unauthorized activity. It works by analyzing network packets and comparing them against a database of known attack signatures, looking for any signs of malicious activity. If it detects something suspicious, it will generate an alert, allowing administrators to investigate the incident and take appropriate action.
There are two main types of IDS:
- host-based and network-based. Host-based IDS (HIDS) run on individual computers, monitoring system activity and detecting any unusual behavior.
- Network-based IDS (NIDS), are placed at strategic points throughout the network, monitoring traffic as it passes by.
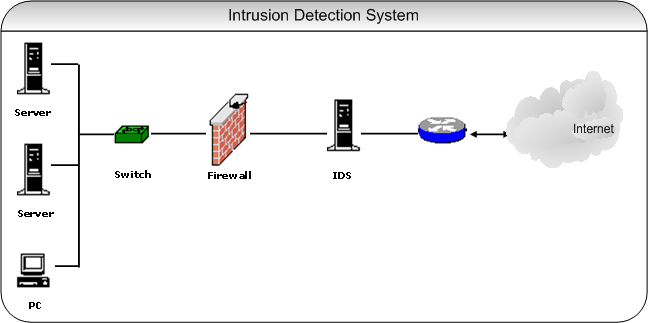
How does an IDS work?
An IDS uses a combination of signature-based and anomaly-based detection to identify potential security threats. Signature-based detection involves comparing network traffic against a database of known attack signatures. These signatures are created by analyzing the behavior of known malware and other types of attacks, allowing the IDS to quickly identify them if they appear on the network.
Anomaly-based detection, on the other hand, involves analyzing network traffic for any patterns that deviate from normal behavior. This can include unusual levels of traffic, unexpected protocols or ports, or other anomalous behavior that could indicate a potential attack.
Once the IDS has detected something suspicious, it will generate an alert, which can be sent to the system administrator via email or other notification methods. The administrator can then investigate the incident and take appropriate action, such as blocking traffic from a specific IP address or disconnecting a compromised device from the network.
Why do you need an IDS?
An IDS is an essential tool for maintaining the security of your network. Without it, you may not even be aware that your network has been compromised until it’s too late. By detecting potential security threats in real time, an IDS can help you respond quickly to minimize the damage caused by an attack.
In addition to detecting attacks, an IDS can also be used to monitor network performance and identify potential bottlenecks or other issues that could impact network performance. This can help you optimize your network and ensure that it’s running at peak efficiency.
Advantages of IDS
- Early detection of attacks: An IDS can detect security threats and attacks in real-time, enabling network administrators to take action before the attack can cause damage.
- Reduced downtime: The quick detection of attacks and an immediate response can minimize the time a system or network is down, reducing business disruptions.
- Centralized monitoring: An IDS provides a centralized location for monitoring multiple systems, making it easier for network administrators to manage network security.
- Cost-effective: Compared to other security measures, such as hiring a dedicated security team or purchasing expensive hardware, IDS can be more cost-effective.
- Customizable: IDS can be customized to meet specific security needs and requirements.
Disadvantages of IDS
- False Positives: An IDS can generate false alarms or alerts, leading to unnecessary investigation and potential system downtime.
- Limited visibility: IDS can only detect attacks that are in their signature database or behavioral baseline. New and unknown threats may not be detected by IDS.
- High skill level required: IDS requires a high level of technical expertise to configure, manage, and monitor effectively.
- Overhead: IDS can put additional overhead on a network, causing slowdowns and delays in data transmission.
- Dependence on updates: An IDS relies on up-to-date signatures and behavioral baselines to detect threats. If updates are not installed regularly, the IDS may miss new threats.
Conclusion
As cyber-attacks become more sophisticated, it’s more important than ever to have robust security measures in place to protect your network. An intrusion detection system is one of the most effective tools available for detecting potential security threats and minimizing the damage caused by an attack. Whether you’re running a small home network or a large corporate infrastructure, an IDS is an essential component of your security toolkit.
An intrusion detection system can be used to monitor the file systems for changes. It is helpful in detecting what changes are made to the system after an attack. An intrusion detection system is used to detect several types of malicious behaviors that can compromise the security and trust of a computer system. We intend to avoid access and keep track of the intruder’s attempts and intentions. Such a system can make a big addition to the security in today’s world to avoid different kinds of attacks like CryptoLocker, WannaCry, and other Ransomware attacks.
hey I need more thing about this intruder system.Can I get a copy of that
Ajay,
You can refer to this post here. You can use share post feature available at the end of the post and mail yourself.