In industrial manufacturing, precision isn’t optional – it’s essential. Among the many processes that define product quality, heat treating stands out as one where temperature control directly determines a metal’s strength, hardness, and reliability. Whether it’s a gear, a shaft, or a load-bearing component, even a small deviation in furnace temperature can alter the material’s microstructure – and with it, its performance and service life.
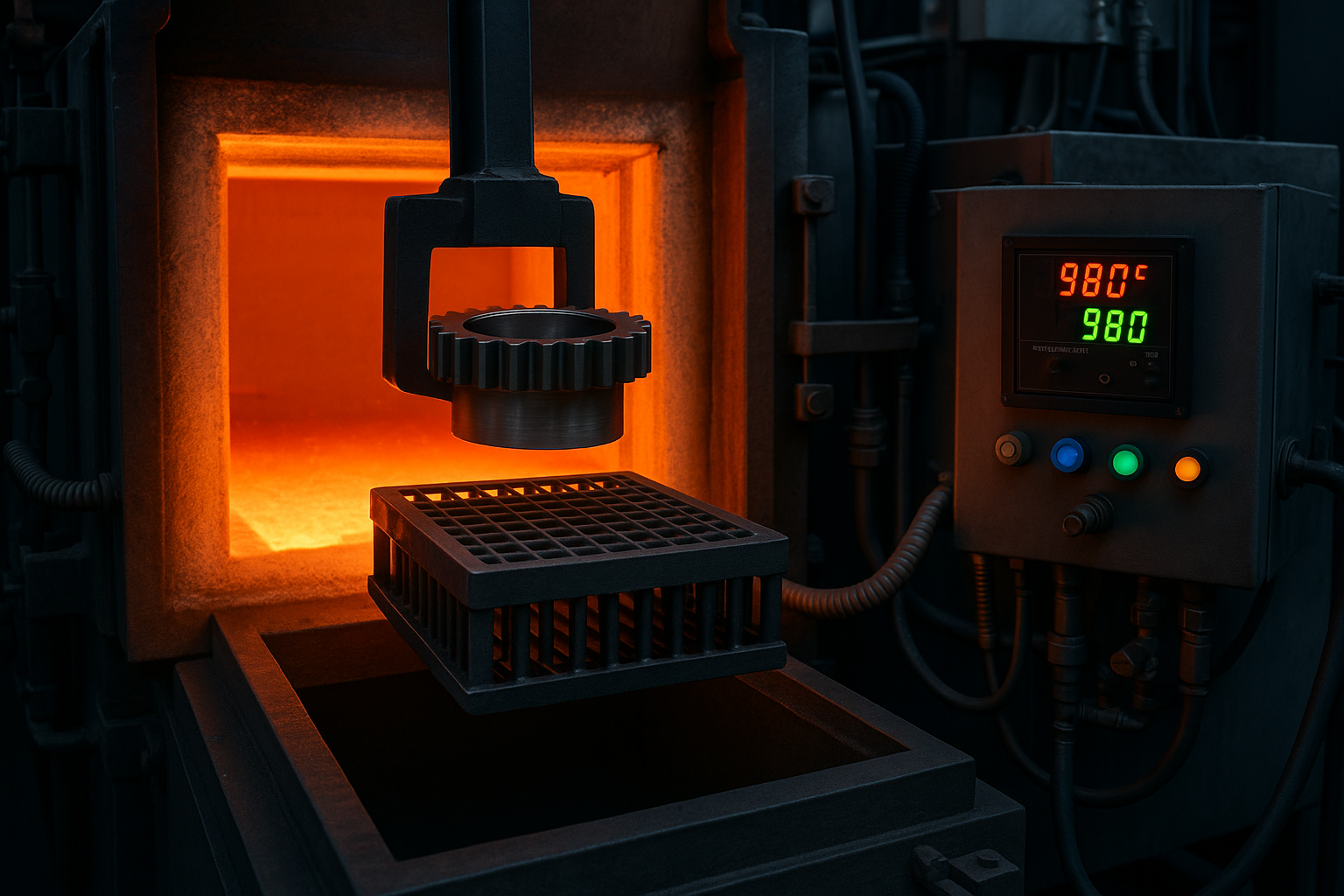
Understanding the Fundamentals of Heat Treating
Heat treating is a controlled thermal process that alters the physical and mechanical properties of metals without changing their shape. The process involves carefully heating and cooling metals at defined rates to achieve desired characteristics such as increased hardness, toughness, wear resistance, fatigue life, and corrosion resistance.
Common methods include carburizing, quenching, tempering, and nitriding, each tailored to achieve specific metallurgical results.
The essence of effective heat treatment lies in temperature control. Every degree matters. Excessive heat can lead to grain growth, distortion, or brittleness, while insufficient heat can cause incomplete hardening or soft spots. Consistent and accurate temperature regulation ensures that metallurgical transformations occur exactly as intended. Read about Laser Cutting.
The Role of Temperature in Metallurgical Transformation
At the core of every heat treatment process lies a phase transformation. When steel is heated beyond its critical temperature, its crystal structure changes from ferrite or pearlite to austenite. Controlled cooling through quenching or tempering locks that structure into a form that delivers the desired hardness or toughness.
Even a variation of just 10 degrees Celsius can significantly affect the outcome. Overheating can cause excessive brittleness and reduced fatigue life, while underheating may leave portions of the material softer than intended. In industries such as automotive, aerospace, and precision engineering, such deviations can lead to premature wear, misalignment, or component failure.
Common Challenges in Temperature Control
Maintaining uniform temperature distribution throughout a furnace load is one of the most demanding aspects of heat treating. Several factors can disrupt consistency:
- Uneven heating zones within furnaces
- Inconsistent airflow or convection patterns
- Incorrect thermocouple placement
- Thermal gradients across large or irregular parts
These inconsistencies can create residual stresses, resulting in warping, cracking, or dimensional distortion after quenching.
Modern furnaces overcome these challenges through multi-zone temperature control systems, high-precision thermocouples, and real-time sensors. Continuous data monitoring and closed-loop feedback ensure that each component in a batch receives identical thermal exposure, guaranteeing consistent metallurgical properties.
How Temperature Control Affects Component Performance
Precise temperature control determines how well components perform under stress. For instance, gears that are improperly heat treated may wear prematurely or fail catastrophically under load. Similarly, shafts may lose alignment tolerance or suffer from fatigue if their surface hardness is inconsistent.
When the process is executed correctly, the benefits are significant:
- Enhanced fatigue resistance
- Improved dimensional stability
- Superior wear and corrosion performance
- Extended service life under high stress
Consistent temperature regulation does not just improve quality – it also reduces scrap rates, rework, and production costs.

Advanced Equipment and Process Integration
Today’s industrial furnaces and heat treatment systems integrate automation, analytics, and sensor technology to maintain exceptional precision. Key advancements include computer-controlled furnaces that manage heating and cooling profiles dynamically, data logging systems for full traceability and quality verification, and predictive maintenance analytics to minimize downtime.
Facilities equipped with multi-zone carburizing furnaces, tempering ovens, and induction systems can process a wide variety of materials and geometries without sacrificing quality. Partnering with specialists in heat treating services ensures that each component undergoes the correct thermal cycle and metallurgical analysis. Providers such as United Gear & Assembly combine gas carburizing, nitriding, and quenching with in-house metallurgical labs to verify results and maintain strict quality standards.
In-House Control and Quality Assurance
Controlling heat treatment in-house offers manufacturers greater oversight of every production stage. It eliminates dependence on third-party vendors, reduces lead times, and allows tighter integration between machining and thermal processing. The ability to monitor and adjust parameters immediately improves consistency and overall production efficiency.
Dedicated metallurgists and technicians analyze microstructures and hardness profiles to verify that each part meets design intent. This level of internal quality control ensures that performance requirements are achieved without compromise.
Conclusion: Precision Defines Performance
Heat treating is both a science and an art. Achieving the desired mechanical properties depends entirely on maintaining precise temperature control throughout every stage—from carburizing and quenching to tempering and nitriding.
In modern manufacturing, precision defines performance. Working with skilled heat treatment specialists—or maintaining in-house expertise—ensures every component receives the exact thermal profile it requires for maximum durability and reliability. Temperature accuracy, process consistency, and metallurgical verification are what separate a satisfactory component from one that performs flawlessly in the field.