Software-Defined Wide-Area Networks (SD-WAN) is a technology that enables the management and operation of wide-area networks (WANs) using software-based approaches rather than relying on traditional hardware-centric methods. SD-WAN provides organizations with greater agility, flexibility, and control over their network infrastructure.
Traditionally, wide-area networks (WANs) were built using dedicated hardware appliances that required manual configuration and management. SD-WAN, on the other hand, leverages software-defined networking (SDN) principles to abstract the network control and management functions from the physical hardware.
SD-WAN allows remote employees to access business applications seamlessly. This is accomplished by combining secure connectivity and network management with software intelligence. SD-WAN can significantly reduce costs and improve performance by offloading data from expensive private circuits onto cheaper broadband or public links such as Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS). In this article, we will unfold how to maximize your return on investment with a managed SD-WAN solution.
PC: juniper.net
The key features and benefits of SD-WAN include:
Quality of Service
Quality of service (Quality of Service) is a set of tools that manage network bandwidth and ensures mission-critical traffic has priority. It also allows enterprises to use their existing network connections and avoid costly upgrades to increase capacity. Quality of service prioritizes business applications and real-time services, VoIP, and video conferencing, giving them high performance over secure and reliable links. This boosts employee productivity and bolsters customer satisfaction.
SD-WAN improves the quality of service by enabling more efficient WAN utilization. It lets IT teams automatically apply operational policies to WAN devices rather than manually configure each device. These policies are based on IP addresses, application profiles, quality-of-service markings, and more. They are pushed from a central control panel to each location’s SD-WAN gateways and routers. This central management enables consistency and ease of implementation across the organization.
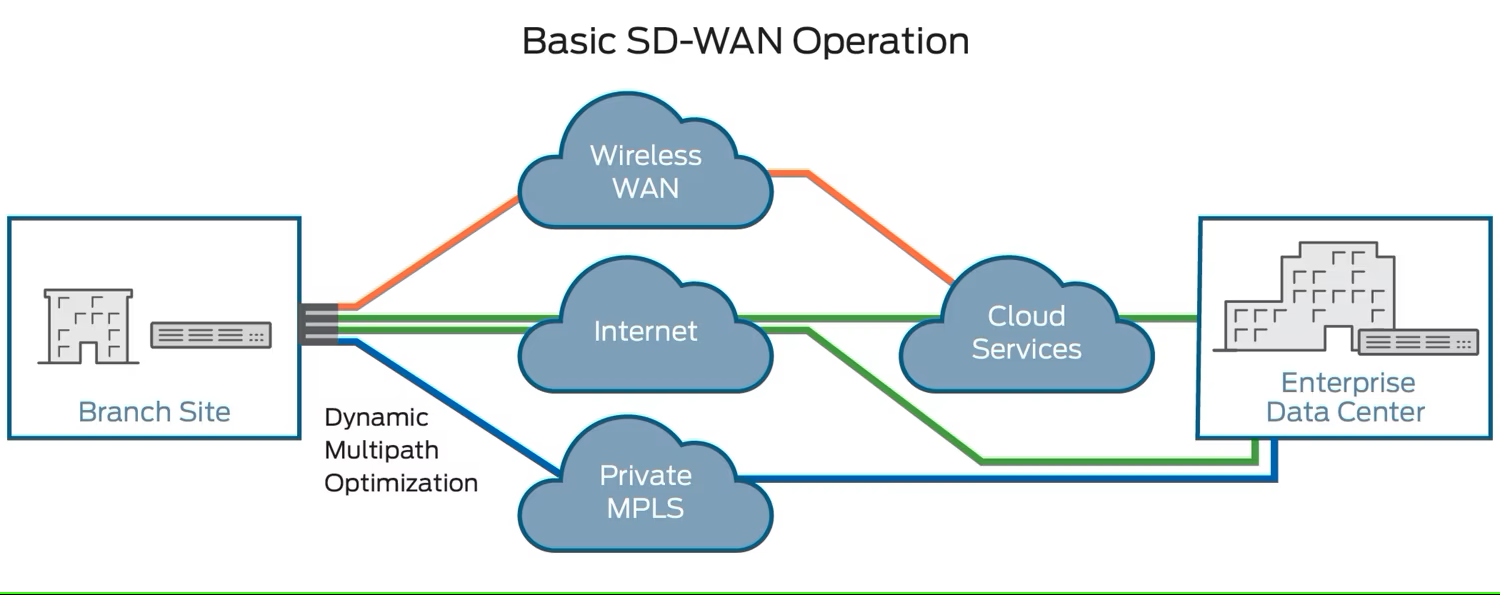
Path intelligence is a crucial aspect of SD-WAN, which can automatically steer traffic over the best-performing connection. This helps reduce jitter, packet loss, and latency. It also minimizes costs by leveraging lower-cost network connections for most traffic and saving expensive MPLS circuits for higher-priority applications. Cloud-based SD-WAN uses its private backbone with points of presence (PoP) worldwide to route traffic reliably and minimize latency without requiring MPLS.
Routing
SD-WAN enables organizations to connect their remote offices and cloud applications at the same time while also optimizing performance. It does this by reducing costs, improving security, and providing flexibility.
The technology replaces traditional routers and WAN optimization features with software. As a result, the technology is scalable and can automatically configure itself to meet various needs without network engineers or administrators needing to adjust them manually. This reduces or eliminates complex, error-prone, and time-consuming manual processes.
For example, an SD-WAN can automatically prioritize business-critical traffic and real-time services, such as Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and video, and then effectively steer them over the best links to ensure the highest quality of experience for end users. It can also monitor WAN link performance, such as latency, jitter, and packet loss, to identify and remediate application delivery issues.
In addition, many SD-WAN solutions incorporate network automation via full-featured APIs to enable easy integration with other infrastructure and software. This allows IT teams to automate manual tasks and improve productivity. It also provides centralized management and global WAN visibility to simplify operations and accelerate various use cases, including hybrid and multi-cloud. The technology can even provide an on-ramp to SaaS and IaaS cloud apps and deliver robust edge security through end-to-end segmentation, centralized policy management, and integrated security VNFs.
Encryption
The centralized control function of an SD-WAN network allows teams to build and deploy operational policies that are automatically pushed to all connected hardware. This helps eliminate the need for multiple separate devices, such as NGFW, IPS, firewalls, and AV, to be installed at each remote site. This also means that centralized teams are less likely to introduce vulnerabilities that could be exploited in a disjointed, site-by-site network.
So, what is SD-WAN configuration? Using the information collected by an SD-WAN, it can be configured to prioritize traffic for critical applications and route them over the most reliable, high-performance connections. This can improve employee productivity, increase staff morale and boost business operations.
SD-WAN can also help businesses cut costs by reducing reliance on expensive private connections. Instead, IT teams can combine an organization’s MPLS circuits with less costly broadband Internet links to provide adequate bandwidth for business-critical applications.
Finally, SD-WAN can enable direct cloud usage at remote branches by eliminating backhauling and connecting each component directly to the data center’s application servers. This significantly reduces connectivity costs, WAN latency, packet loss, and bandwidth requirements. It can also improve cloud application performance by prioritizing business-critical traffic and enabling remote sites to access cloud services over their local Internet connections rather than through the central data center. This can help businesses gain better ROI on their cloud investment. Read more about cloud computing.
Security
SD-WAN is a software-based solution that runs on top of an existing hardware network, allowing networking professionals to change and manage policies from a single administrator location. This reduces the amount of time required to implement and update WAN capabilities.
A traditional WAN model relies on routing protocols to assign a path to data packets, which could be more efficient and cloud-friendly. Instead, an SD-WAN architecture identifies and prioritizes applications to optimize data transfer speeds and enhance user experiences.
Additionally, SD-WAN technology provides a security layer that prevents attacks by separating traffic from different locations and devices. The separation, known as micro-segmentation, helps IT staff isolate and secure sensitive data and ensure that employees can access critical applications.
As the network expands, an SD-WAN can use multiple links in each location to create redundancies. This helps organizations reduce IT costs while ensuring data transfers are not interrupted during a transport outage.
An SD-WAN also supports the integration of VPN to securely connect remote employees to corporate networks, which enables them to work from home or while traveling on business. This benefits employees who need to access critical resources, even when their internet connection or cellular service is down. In addition, an SD-WAN can support secure local internet breakout of SaaS and IaaS applications to help ensure that they are not sending sensitive data across the public internet.
Cost optimization
SD-WAN can leverage multiple network connections, including cost-effective internet links, to provide high-quality network connectivity at a lower cost compared to traditional MPLS-based WANs.
Wrapping Up
SD-WAN has gained significant popularity in recent years due to its ability to simplify network management, improve application performance, and reduce costs. It is particularly beneficial for organizations with distributed branch locations, remote workers, or those adopting cloud-based applications and services.