This Java login application follows MVC architecture and consists of Java servlets, and JSPs. It uses the MySQL database server to refer to the user details. The input fields are validated using javascript.
What is a Model View Controller architecture?
The model (DAO) consists of application data and business rules, and the controller (Servlet) acts as an interface between views and the model. It mediates input, converting it to commands for the model or view. A view (JSP) can be any output representation of data, such as a chart or a diagram, generally HTML or JSP page.
Here DAO is the Data Access Object – This part concentrates on business logic and database server connections and operations.
Use any IDE – Integrated development environment to minimize your work. If you haven’t started using any IDE, go get one. You will fall in love with it. I would recommend you use Eclipse for Java applications. Link to download Eclipse. It is an open-source tool.
This application is explained thoroughly with appropriate comments and tested in Eclipse IDE. Please write comments if you find any difficulty while understanding the application.
Suggested Read:
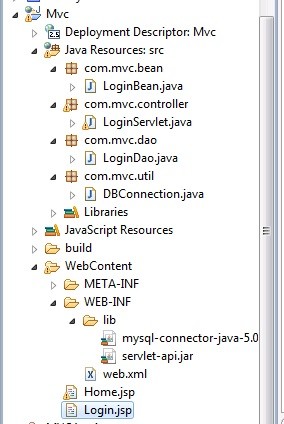
It is advised to segregate different components in a standard directory structure as shown below. Start your programming with New Project -> dynamic web application project type.
Subscribe to our channel
Login details are forwarded to LoginServlet from the Login.jsp page. When you click on the Login button the request is forwarded to the page which is mentioned in the action tag of the form so here the request will be forwarded to LoginServlet.java class.
Login.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>Login</title>
<script>
function validate()
{
var username = document.form.username.value;
var password = document.form.password.value;
if (username==null || username=="")
{
alert("Username cannot be blank");
return false;
}
else if(password==null || password=="")
{
alert("Password cannot be blank");
return false;
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div style="text-align:center"><h1>Login application in Java using MVC and MySQL </h1> </div>
<br>
<form name="form" action="LoginServlet" method="post" onsubmit="return validate()">
<!-- Do not use table to format fields. As a good practice use CSS -->
<table align="center">
<tr>
<td>Username</td>
<td><input type="text" name="username" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Password</td>
<td><input type="password" name="password" /></td>
</tr>
<tr> <!-- refer to the video to understand request.getAttribute() -->
<td><span style="color:red"><%=(request.getAttribute("errMessage") == null) ? ""
: request.getAttribute("errMessage")%></span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td><input type="submit" value="Login"></input><input
type="reset" value="Reset"></input></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
LoginServlet.java
package com.mvc.controller;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.mvc.bean.LoginBean;
import com.mvc.dao.LoginDao;
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
public LoginServlet() // default constructor
{
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//Here username and password are the names which I have given in the input box in Login.jsp page. Here I am retrieving the values entered by the user and keeping in instance variables for further use.
String userName = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
LoginBean loginBean = new LoginBean(); //creating object for LoginBean class, which is a normal java class, contains just setters and getters. Bean classes are efficiently used in java to access user information wherever required in the application.
loginBean.setUserName(userName); //setting the username and password through the loginBean object then only you can get it in future.
loginBean.setPassword(password);
LoginDao loginDao = new LoginDao(); //creating object for LoginDao. This class contains main logic of the application.
String userValidate = loginDao.authenticateUser(loginBean); //Calling authenticateUser function
if(userValidate.equals("SUCCESS")) //If function returns success string then user will be rooted to Home page
{
request.setAttribute("userName", userName); //with setAttribute() you can define a "key" and value pair so that you can get it in future using getAttribute("key")
request.getRequestDispatcher("/Home.jsp").forward(request, response);//RequestDispatcher is used to send the control to the invoked page.
}
else
{
request.setAttribute("errMessage", userValidate); //If authenticateUser() function returnsother than SUCCESS string it will be sent to Login page again. Here the error message returned from function has been stored in a errMessage key.
request.getRequestDispatcher("/Login.jsp").forward(request, response);//forwarding the request
}
}
}
LoginDao.java
package com.mvc.dao;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import com.mvc.bean.LoginBean;
import com.mvc.util.DBConnection;
public class LoginDao {
public String authenticateUser(LoginBean loginBean)
{
String userName = loginBean.getUserName(); //Assign user entered values to temporary variables.
String password = loginBean.getPassword();
Connection con = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
String userNameDB = "";
String passwordDB = "";
try
{
con = DBConnection.createConnection(); //Fetch database connection object
statement = con.createStatement(); //Statement is used to write queries. Read more about it.
resultSet = statement.executeQuery("select userName,password from users"); //the table name is users and userName,password are columns. Fetching all the records and storing in a resultSet.
while(resultSet.next()) // Until next row is present otherwise it return false
{
userNameDB = resultSet.getString("userName"); //fetch the values present in database
passwordDB = resultSet.getString("password");
if(userName.equals(userNameDB) && password.equals(passwordDB))
{
return "SUCCESS"; ////If the user entered values are already present in the database, which means user has already registered so return a SUCCESS message.
}
}
catch(SQLException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "Invalid user credentials"; // Return appropriate message in case of failure
}
}
}
LoginBean.java
JavaBeans are classes that encapsulate many objects into a single object. This object facilitates to access or set all the members of this class. The bean class contains only setters and getters usually.
package com.mvc.bean;
public class LoginBean
{
private String userName;
private String password;
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
The database name is customers and the table name is users. If you take a look at the video, we are using the MySQL database server that comes as part of WAMP software (works for Windows OS). It is a freeware, just download, install, and use it. As an alternative, you can download the MySQL server from the official website. You can use any other database server also.

DBConnection.java
We are using the MySQL database in this application. We can use any database server that supports Java. Appropriate driver and connection URLs should be used based on the database you choose.
Note: Don’t forget to add the dependent jar for the database server. In our case it’s mysql-connector-java.jar.
package com.mvc.util;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
public class DBConnection {
public static Connection createConnection()
{
Connection con = null;
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/customers"; //MySQL URL and followed by the database name
String username = "root"; //MySQL username
String password = "root123"; //MySQL password
try
{
try
{
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //loading mysql driver
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password); //attempting to connect to MySQL database
System.out.println("Printing connection object "+con);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
}
web.xml
The web.xml is known as a deployment descriptor. It lists all the servlets used in the application. Do remember to give a full class name in the servlet-class.
It features few additional configurations such as a welcome-file name leading to the mentioned file name when this application is loaded.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="2.5">
<display-name>LoginMvc</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>Login.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<description></description>
<display-name>LoginServlet</display-name>
<servlet-name>LoginServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.mvc.controller.LoginServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>LoginServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/LoginServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet>
<description></description>
<display-name>LogoutServlet</display-name>
<servlet-name>LogoutServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.mvc.controller.LogoutServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>LogoutServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/LogoutServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Home.jsp
An example of a user home page after successful log-in.
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<title>Home Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<center><h2>Home Page</h2></center>
Welcome <%=request.getAttribute("userName") %> <!-- Refer to the video to understand how this works -->
<div style="text-align: right"><a href="LogoutServlet">Logout</a></div>
</body>
</html>
LogoutServlet.java
This is an example of a logout feature. After clicking on logout, the user will be redirected to Login.jsp.
package com.mvc.controller;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
public class LogoutServlet extends HttpServlet
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException
{
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false); //Fetch session object
if(session!=null) //If session is not null
{
session.invalidate(); //removes all session attributes bound to the session
request.setAttribute("errMessage", "You have logged out successfully");
RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher("/Login.jsp");
requestDispatcher.forward(request, response);
System.out.println("Logged out");
}
}
}
Many users were asking for the role-based login application. I have made a post recently for the Session and Role-based Java Login example.
Sir, Thanks you so much for help me.I dont have any word for you that much help got from this example.
Thanks, Dinesh.
You are always welcome here. I am going to write more such examples.
Hi Ravi,
I have uploaded image in a folder and stored its path in the database. While displaying it, I am accessing the path from database and giving it in anchor tag so when it is clicked the image should get open. But it is not. I have checked for the path and the path is exactly correct. And I have tried to just display image by using img tag, it works fine in eclipse browser but when I open it in chrome it does not get displayed.
I am not understanding this behaviour. Please give any idea. The path that I am storing in the database is correct and I want the image to get open when it is given in anchor tag.
Thank You.
Manasa,
I have to look into the code to find out the issue. Can you email your code to me?
Hi Ravi,
I need you email id.
Thank you.
[email protected]
mansa can you send same code to my mail because i am also facing same problem
[email protected]
Hi,
Consider after successful login, I will redirect the page to home.jsp where the person who has logged in can enter the employee details. To do this should I have create a separate servlet and DAO file? How to do this? Please give me a brief idea.
Thank you.
Good question.
It depends on what operation you would like to implement. If you would just want to display a form where user can enter details and submit, for this you can have a JSP and after submitting, you could either go to same servlet but call a different method there and then the DAO class. There are many ways to do this.
On the other hand, if you just want to display some results, you could do this using JSP tags either on the same JSP or a link to another one.
Hi Ravi,
I created separate servlet and DAO files to add employee details into the database. Worked fine and was able to understand the flow.
Thank you.
Great.!! Good luck ahead!
And also I am not able to understand request.getAttribute() and setAttribute. Can you give an example and explain?
Thank you.
It works as a key-Value pair.
In the servlet, you are writing
request.setAttribute("userName", userName)and you are accessing this value via key “userName” in the Home.jsp
request.getAttribute("userName")Go to this link, it is explained here. https://youtu.be/_WLeWa7mjHw?t=5m10s
Hi Ravi,
Whenever we call servlet using form, control automatically goes to doPost() in servlet. How can we call a specific function in servlet as it contains only doGet() and doPost()? If we can do that please explain us how?
Thank you.
Hi Manasa,
Very good question and welcome back.
You can have only the methods which are present in the parent class i.e. HttpServlet.
The HttpServlet class contains the methods – doGet, doPost, doPut, doDelete, init, destroy, getServletInfo.
You can follow one of these 2 methods to customize your code.
1. For Get method:
Inside a JSP:/AddTestServlet?type=createTest">Create Test
Inside a servlet:
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
String type=request.getParameter("type");
if (type.equals("createTest"))
For Post method:
2. You can redirect your requests to a common method and implement your logic.
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {process(request,response);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
process(request,response);
public void process(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response)
{ ......
}
Hi Ravi,
I have added a photo to the database and able to access and display it. But when I want to edit it, there occurs a prblm. In jsp I have dis code and in action i am giving control to EditServlet.
//for displaying photo and in source i have given control to ImageServlet so that image can be displayed
photo
<img src="ImageServlet?id=” name=”editphoto” height=”50px” width=”50px”>
//for changing photo
Change photo here
When i use this code, I have to edit photo otherwise it stores null in the database. I mean if I add a new photo it takes that photo and stores it in database otherwise if I change other parameters and not the photo it takes null. I am accessing the ‘file’ in the EditServlet and updating it. If I give a new photo over there it works allright but when i dont want to edit it, it takes null. I am getting to know that as I am not giving any values,it takes null but I dont want that to happen. I want previous image to be displayed. How can I give the condition for it. I thought since I have given control to the ImageServlet for displaying, it will store the previous image even though I dont edit it. I hope my question is clear.
I need help in this.
Thank you.
photo
<img src="ImageServlet?id=” name=”editphoto” height=”50px” width=”50px”>
Change photo here
This is the code
Hi Ravi,
Thanks I got how to call another function in the servlet. When we are calling like this can we pass the data to it? I mean we are calling process(request,response) so here can we pass the data to process()?
Thank you.
Yes, Manasa.
You can do that.
Hi Ravi,
I have a doubt. Consider that I have added registered users details successfully into the database and I have fetched the details from database and displayed and also I have given modify and delete button to each of it. Now when I click modify of particular row that particular name and password should be displayed. For this I am doing all the database operations in the jsp page and displaying it. Is this wrong pattern of mvc? If I have to user servlets how can I do that?
Hi Manasa,
You can edit it in the JSP page. There is no need to traverse through servlet for every small operation.
If you want to go via servlet, when you click on modify button, you need to have a link to servlet Modify. From here you can implement the same logic.
What is @webservlet? When this statement is there in servlet, whatever mapping i do in web.xml does not affect anything. I mean the servlets dont even run? Why is this?
Hi Manasa,
@WebServlet is the annotation used to declare a servlet.
I don’t see it in the LoginServlet.
I think it is added by Eclipse automatically in your case. I am not sure about the issue you are facing.
Every new servlet needs to be mentioned in the web.xml. Whenever a servlet gets compiled, the web.xml is referred.
Thanks Ravi.
It worked fine for me. This really has helped me a lot in how to go about in mvc coding. It has solved lots of confusions that I had in mvc coding.
You are welcome Manasa.
I’m glad it helped you.
You may like to go through role based login application as well at this point – https://krazytech.com/programs/session-role-based-java-login-example
Video- https://youtu.be/swdx5g0X1hk