Mobile Ad hoc networks (MANETs) are a new paradigm of wireless network, offering unrestricted mobility without any underlying infrastructure such as base station or mobile switching centers. Basically ad hoc network is a collection of nodes communicating with each other by forming a multi-hop network. In a mobile ad hoc network, it is much more vulnerable to attacks than a wired network due to its limited physical security, dynamically changing network topology, energy constrained operations and lack of centralized administration. Since all the nodes in the network collaborate to forward the data, the wireless channel is prone to active and passive attacks by malicious nodes, such as Denial of Service (DoS), eavesdropping, spoofing, etc. The intent of this paper is to investigate the security goal, security challenges and different types of active and passive attacks on MANETs.
1.INTRODUCTION
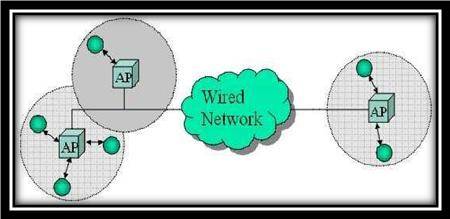
With the proliferation of cheaper, small and more powerful mobile devices, mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs) have become one of the fastest growing areas of research. A Mobile ad hoc network is a system of wireless mobile nodes with routing capabilities – the union of which form an arbitrary graph. Any group of them are capable of forming an autonomous network that require no infrastructure and is capable of organizing itself into arbitrary changeable topologies. Such a network may operate in a stand-alone fashion, or may be connected to the larger Internet[Figure1,2]. The definition, which is given by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).Minimal configuration and quick deployment make ad hoc networks suitable for emergency situations like natural or human-induced disasters, military conflicts, emergency medical situations etc. Unlike traditional mobile wireless networks, Ad hoc networks dont rely on any fixed infrastructure(base stations, access points). This flexibility makes them attractive technology for many applications such as rescue and tactical operations, disaste recovery operations and educational applications where we can setup virtual class or conferences.
Figure1: Infrastructure based
The following are the advantages of MANETs:-
- They provide access to information and services regardless of geographic position.
- These networks can be set up at any place and time.
- These networks work without any pre-existing infrastructure.
Figure2: Infrastructure less
Security has become a primary concern in order to provide protected communication between nodes in a potentially hostile environment. In a mobile ad hoc network, it is much more vulnerable to attacks than a wired network due to its limited physical security, volatile network topologies, power-constrained operations, and lack of centralized monitoring and management point.
2. APPLICATIONS OF MANETS :
With the increase of portable devices as well as progress in wireless communication, ad hoc networking is gaining importance with the increasing number of widespread application.
2.1.MANET Applications Military
Ad hoc networking would allow the military to take advantage of commonplace network technology to maintain an information network between the soldiers, vehicles, and military information head quarters. Consider a scenario as shown in figur-3, is deployed over a battlefield . The ad hoc network formed by the air vehicle in the sky can provide a backbone for land based platforms to communicate when they are out of direct range,or when obstacles prevent direct communication. The ad hoc network therefore extends down to the land based forces and allows communication across the battlefield. Voice and video, as well as sensing and data applications can be supported.
Figure 3: Military Applications
2.2.MANET Applications Disaster Relief
In cases of disasters, the existing infrastructure is often damaged or destroyed. Natural disasters e.g. lead to the loss of electricity and Internet connectivity, as described in Figure 4. Emergency rescue operations must take place where non-existing or damaged communications infrastructure and rapid deployment of a communication network is needed. An ad hoc network can be used used in emergency/rescue operations for disaster relief efforts, e.g. in fire, flood, or earthquake, to overcome the problems incurred by missing infrastructure, helping to better cope with the consequences of such calamities. Mobile units carry networking equipment to support routing operations.Information is relayed from one rescue team member to another over a small handheld. Other commercial scenarios include e.g. ship-to-ship ad hoc mobile communication, law enforcement etc.
Figure 4: Disaster Relief Applications
3.CHALLENGES IN SECURING THE MANETs:
MANETs are much more vulnerable to attack than wired network. This is because of following reasons:
3.1 Absence of Infrastructure
Ad hoc networks operate independently of any infrastructure, which makes inapplicable any classical solutions based on certification authorities and on line servers.
3.2 Limited physical security
Mobile wireless networks are generally more prone to physical security threats than a fixed-cable nets. The increased possibility of eavesdropping, spoofing, and denial-of-service attacks should be carefully considered. Existing link security techniques are often applied within wireless networks to reduce security threat.
3.3 Restricted power Supply
Due to mobility of nodes in the ad hoc network, nodes will rely on battery as their power supply method, the problem that may be caused by restricted power supply is denial-of-service attacks and selfish manner.
3.4 Dynamically changing network topology
Nodes are free to move arbitrarily. The network topology may change randomly and have no restriction on their distance from other nodes. As a result of this random movement, the whole topology is changing in an unpredictable manner, which in turn gives rise to both directional as well as unidirectional links between the nodes as shown in figure 5.
Figure 5: changing network topology
3.5 Lack of Centralized monitoring
Absence of any centralized monitoring makes the detection of attacks a very difficult problem because it is not easy to monitor the traffic in a highly and large scale ad hoc network . It is rather common in the ad hoc network that benign failures such as transmission impairments and packet dropping.
4. SECURITY GOALS IN ADHOC NETWORKS
The goals of security mechanism of MANETs are similar to that of other networks. Security is a great issue in network especially in MANETs where security attacks can affect the nodes limited resources and consume them or waste the time before rote chain broke. Security is a vectored term of multi systems, procedures and functions that works together to reach certain level of security attributes[6].
Figure 6: Types of Security Goals
4.1 Availability
The main goal of availability is to node will be available to its users when expected, i.e. survivability of network services despite denial of service attack. For example, on the physical and media access control layers, an adversary could employ jamming to interfere with communication on physical channel while on network layer it could disrupt the routing protocol and continuity of services of the network. Again, in higher levels, an adversary could bring down high-level services such as key management service, authentication service .
4.2 Confidentiality
The goal of confidentiality is to keeping information secret from unauthorized user or nodes. In other words, ensures payload data and header information is never disclosed to unauthorized nodes. The standard approach for keeping information confidential is to encrypt the data with a secret key that only intended receivers posses, hence achieving confidentiality.
4.3 Integrity
The goal of integrity is to guarantee the message being transmitted is never corrupted. Integrity guarantees the identity of the messages when they are transmitted. Integrity can be compromised mainly in two ways .
Malicious altering:– A message can be removed, replayed or revised by an adversary with malicious goal.
Accidental altering:- if the message is lost or its content is changed due to some benign failures, which may be transmission errors in communication or hardware errors such as hard disk failure.
4.4 Authentication
The goal of authentication is too able to identify a node with which it is communicating and to prevent impersonation. In infrastructure-based wireless network, it is possible to implement a central authority at a point such as base station or access point. But in MANETs, no central administration so it is difficult to authenticate an entity.
4.5 Non repudiation
The main goal of non repudiation is sender of a message cannot deny having sent the message. This is useful when for detection and isolation of compromised nodes. When node P receives an erroneous message from Q, non repudiation allows P to access Q using this message and to convince other nodes that Q is compromised.
4.6 Authorization
Authorization is a process in which an entity is issued a credential, which specifies the privileges and permissions it has and cannot be falsified, by the certificate authority. Authorization is generally used to assign different access rights to different level of users.
5.SECURITY ATTACKS ON MANET
Malicious and selfish nodes are the ones that fabricate attacks against physical, data link, network, and application-layer functionality [Fig-7]. Current routing protocols are exposed to two types of attacks
1.Active attacks
In a active attack, information is inserted to the network and thus the network operation or some nodes may be harmed. Through which the misbehaving node has to bear some energy costs in order to perform some harmful operation, and Nodes that perform active attacks with the aim of damaging other nodes by causing network outage are considered to be malicious.
2.Passive attacks
In a passive attack, a malicious node either ignores operations supposed to be accomplished by it. That mainly consists of lack of cooperation with the purpose of energy saving Nodes that perform passive attacks with the aim of saving battery life for their own communications are considered to be selfish. Selfish nodes can severely degrade network performances and eventually partition the network .
Figure 7: Classification of Attacks
5.1.Denial of service (Data link Layer Attach):
In this attack malicious node floods irrelevant data to consume network bandwidth or to consume the resources (e.g. power, storage capacity or computation resource) of a particular node. With fixed infrastructure networks, we can control denial of service attack by using Round Robin Scheduling, but with mobile ad hoc networks, this approach has to be extended to adapt to the lack of infrastructure, which requires the identification of neighbor nodes by using cryptographic tools, and cost is very high.
For example, consider the following Fig. 8. Assume a shortest path exists from X to Z and R and Z cannot hear each other, that nodes Q and R cannot hear each other, and that Y is a malicious node attempting a denial of service attack. Suppose X wishes to communicate with Z and that X has an unexpired route to Z in its route cache. Transmits a data packet toward Z with the source route X –> P –> Q –> Y –> R –> S –> Z contained in the packets header. When Y receives the packet, it can alter the source route in the packets header, such as deleting S from the source route. Consequently, when R receives the altered packet, it attempts to forward the packet to Z. Since Z cannot hear R, the transmission is unsuccessful.
Figure 8: Denial of service attack
5.2.Tunneling /Wormhole(Network layer attack):
Tunneling attack is also called wormhole attack. In a tunneling attack, an attacker receives packets at one point in the network, tunnels them to another point in the network, and then replays them into the network from that point. It is called tunneling attack because the colluding malicious nodes are linked through a private network connection which is invisible at higher layers [Fig-9].
Figure 9: Wormhole Attack
5.3.Sybil attack :
Malicious nodes in a network may not only impersonate one node, they could assume the identity of several nodes, by doing so undermining(destroy) the redundancy(repeating) of many routing protocols. This attack is called the Sybil attack. Sybil attack tries to degrade the integrity of data, security and resource utilization that the distributed algorithm attempts to achieve. Sybil attack can be performed for storage, routing mechanism, air resource allocation and misbehavior detection. Basically, any peer-to-peer network (especially wireless adhoc networks) is vulnerable to Sybil attack.
Figure 10: Sybil Attack
Table : Security Solutions for MANETs.
| Layer | Attacks | Solution |
| Application
Layer |
Repudiation, data corruption | Detecting and
preventing virus, worms, malicious codes and application abuses by use of Firewalls, IDS. |
| Transport
Layer |
Session hijacking, SYN Flooding | Authentication and securing end-to-end or point-to-point
communication use of public cryptography(SSL, TLS, PCT) etc. |
| Network
Layer |
Routing protocol attacks (e.g. DSR, AODV etc.),Wormhole, blackhole, Byzantine, flooding, resource consumption, location disclosure attacks | Protecting the ad
hoc routing and forwarding protocols |
| Data Link
Layer |
Traffic analysis, monitoring, disruption MAC (802.11), WEP weakness etc. | Protecting the wireless MAC
protocol and providing link layer security support. |
| Physical Layer | Eavesdropping, Jamming,
Interceptions. |
Preventing signal jamming denial-of-service attacks by using Spread
Spectrum Mechanism. |
6. CONCLUSION
Importance of MANET cannot be denied as the world of computing is getting portable and compact. Mobile ad hoc Network have the ability to setup networks on the fly in a harsh environment where it may not possible to deploy a traditional network infrastructure. Security is not a single layer issue but a multilayered issue. Due to mobility and open media nature, the mobile ad hoc networks are much more prone to all kinds of security risks, such as information disclosure, intrusion, or even denial of service. As a result, the security needs in the mobile ad hoc networks are much higher than those in the traditional wires networks. It requires a multi fence security solution that provides complete security spanning over the entire protocol stack. The Security research area is still open as many of the provided solutions are designed keeping a limited size scenario and limited kind of attacks and vulnerabilities. MANET are the future networks.because they are practically versatile ,easy to use,inexpensive and can instantly updates and reconfigures itself. In this post we have highlighted the some typical vulnerability which are caused by characteristics of mobile ad hoc networks such as dynamic topology, limited resources (e.g. bandwidth, power), lack of central managements points. And finally we discussed active and passive security attacks on each layer and their solutions.

How can I do a project in adhoc network…. Can u help me???
hello sir,
can i take this topic for final SEM seminar(BE ECE)???
i am feeling this topic is bit confused!!
please reply
Ad Hoc Networks and securing it is indeed a good topic.
good
Thanks for your comments Chitra..
Comments are closed.